【pytorch】Animatable 3D Gaussian+源码解读(一)_animatable gaussians-程序员宅基地
概述
创新点:
- 多人场景 无遮挡处理
- 以3DGS进行表达
方法:
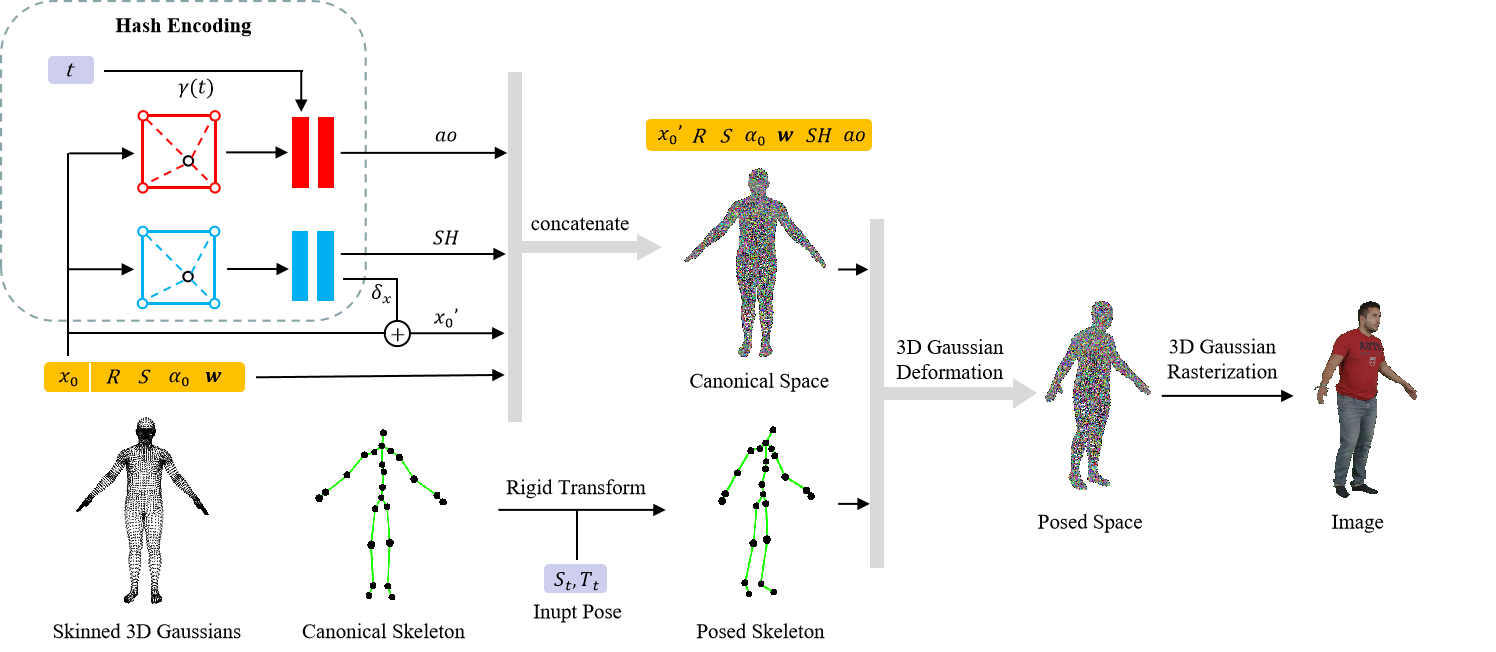
环境配置
基本和3DGS的配置差不多…
pip install torch==1.13.1+cu117 torchvision --index-url https://download.pytorch.org/whl/cu117
pip install hydra-core==1.3.2
pip install pytorch-lightning==2.1.2
pip install imageio
pip install ./submodules/diff-gaussian-rasterization
pip install ./submodules/simple-knn
pip install git+https://github.com/NVlabs/tiny-cuda-nn/#subdirectory=bindings/torch
子模块记得 git clone --recursive 多次踩坑…
tinycudann建议先git到本地…
数据准备
|---data
| |---Gala
| |---PeopleSnapshot
| |---smpl
下载以后挨个解压,整理成格式
单个数据集结构:
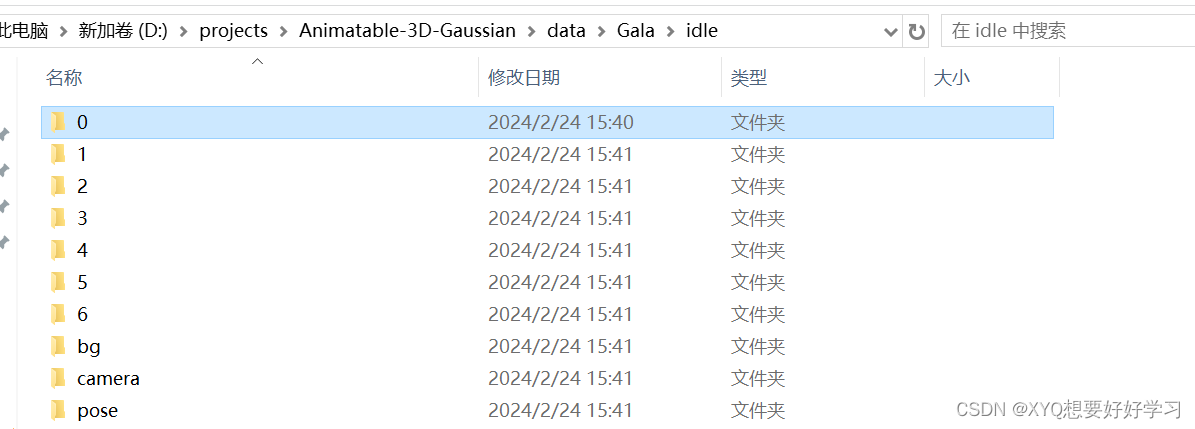
0-6代表不同相机序号——同一视频的不同视角
每个文件夹均有对应的300帧+300mask。
bg定义了7个相机视角下的背景,目前还不知道有什么用,后续看看…

camera文件夹下是7个文本文件,描述相机参数。具体的表示在【pytorch】Animatable 3D Gaussian+源码解读(二)中分析。
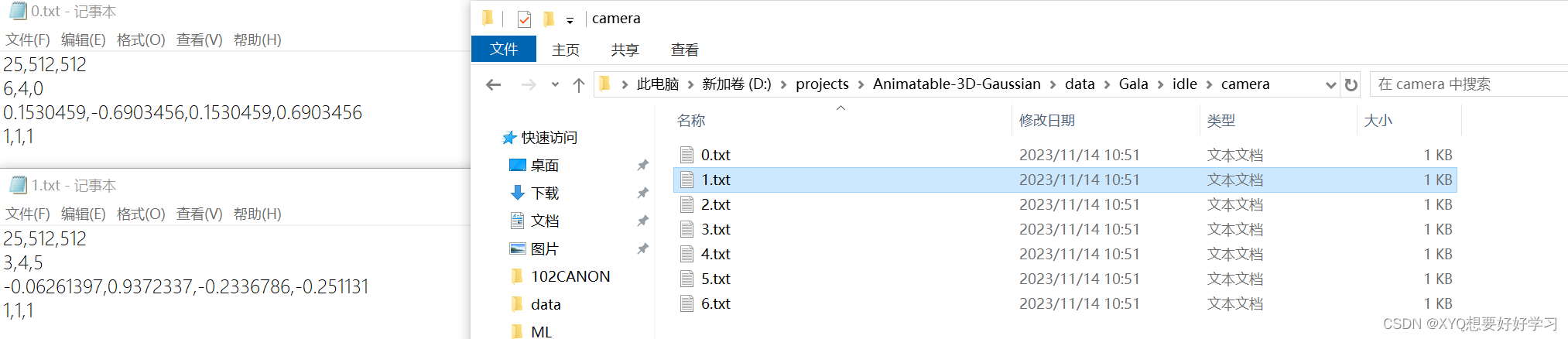
pose文件夹下是300个文本文件,分别描述300帧中300个pose。
此外,Gala数据集中还有一个名为model的文件夹需要注意:
应该是定义了人体标准模板,包括网格、tpose、蒙皮权重等…
model_path (str) : The path to the folder that holds the vertices, tpose matrix, binding weights and indexes.
数据集具体是怎么利用的我们再结合代码来看看…
代码解读
先跟着debug走一遍流程… 然后再以面向对象的思路把握全局
Define Gaussian
首先定义场景表达元素:高斯球
train.py:
model = NeRFModel(opt)
nerf_model.py:
class NeRFModel(pl.LightningModule):
def __init__(self, opt):
super(NeRFModel, self).__init__()
self.save_hyperparameters() # 储存init中输入的所有超参
self.model = hydra.utils.instantiate(opt.deformer)
此处,opt.deformer==Gala模型:
Since the public dataset [1] contains few pose and shadow changes, we create a new dataset named GalaBasketball in order to show the
performance of our method under complex motion and dynamic
shadows.
正文开始:
"""
Attributes:
parents (list[J]) : Indicate the parent joint for each joint, -1 for root joint.
bone_count (int) : The count of joints including root joint, i.e. J.
joints (torch.Tensor[J-1, 3]) : The translations of each joint relative to the parent joint, except for root joint.
tpose_w2l_mats (torch.Tensor[J, 3]) : The skeleton to local transform matrixes for each joint.
"""
初始化函数:
"""
Init joints and offset matrixes from files.
Args:
model_path (str) : The path to the folder that holds the vertices, tpose matrix, binding weights and indexes.
num_players (int) : Number of players. # 多人场景
"""
由此模型超参数为:
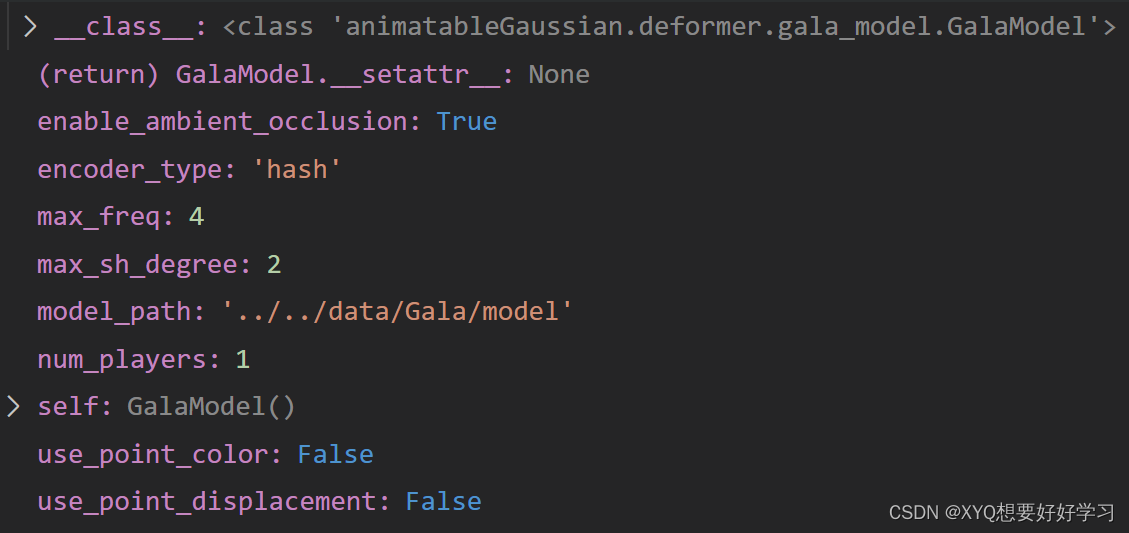
首先是一些人体基本操作——读取相关数据:
model_file = os.path.join(model_path, "mesh.txt")
vertices, normals, uvs, bone_weights, bone_indices = read_skinned_mesh_data(
model_file)
tpose_file = os.path.join(model_path, "tpose.txt")
tpose_positions, tpose_rotations, tpose_scales = read_bone_joints(
tpose_file)
tpose_mat_file = os.path.join(model_path, "tpose_mat.txt")
tpose_w2l_mats = read_bone_joint_mats(tpose_mat_file)
joint_parent_file = os.path.join(model_path, "jointParent.txt")
self.joint_parent_idx = read_bone_parent_indices(joint_parent_file)
self.bone_count = tpose_positions.shape[0]
self.vertex_count = vertices.shape[0]
print("mesh loaded:")
print("total vertices: " + str(vertices.shape[0]))
print("num of joints: " + str(self.bone_count))
read_skinned_mesh_data(“mesh.txt”)函数读取顶点、蒙皮权重、UV坐标;
read_bone_joints(“tpose.txt”)函数读取关节数据;
read_bone_joint_mats(“tpose_mat.txt”)读取world-to-local转化矩阵;
read_bone_parent_indices(“jointParent.txt”)读取关节父子关系。
多人扩维模板复制:
self.register_buffer('v_template', vertices[None, ...].repeat(
[self.num_players, 1, 1]))
uvs = uvs * 2. - 1.
self.register_buffer('uvs', uvs[None, ...].repeat(
[self.num_players, 1, 1]))
bone_weights = torch.Tensor(
np.load(os.path.join(model_path, "weights.npy")))[None, ...].repeat([self.num_players, 1, 1])
self.register_buffer("bone_weights", bone_weights)
1.register_buffer:定义一组参数,该组参数的特别之处在于:模型训练时不会更新(即调用 optimizer.step() 后该组参数不会变化,只可人为地改变它们的值),但是保存模型时,该组参数又作为模型参数不可或缺的一部分被保存。
2.[None,…]:多一维
# 关节位置申请加入训练
self.J = nn.Parameter(
tpose_positions[None, ...].repeat([self.num_players, 1, 1]))
self.tpose_w2l_mats = tpose_w2l_mats
# 顶点归一化
minmax = [self.v_template[0].min(
dim=0).values * 1.05, self.v_template[0].max(dim=0).values * 1.05]
self.register_buffer('normalized_vertices',
(self.v_template - minmax[0]) / (minmax[1] - minmax[0]))
# distCUDA2 from simple_knn 计算点云中的每个点到与其最近的K个点的平均距离的平方
dist2 = torch.clamp_min(
distCUDA2(vertices.float().cuda()), 0.0000001)[..., None].repeat([1, 3])
然后开始处理要训练的高斯:
定义顶点偏移:
using unconstrained per-vertex displacement can easily cause the optimization process to diverge in dynamic scenes.Therefore, we also model a parameter field for vertex displacement. F.
# x0 → δx
if use_point_displacement:
self.displacements = nn.Parameter(
torch.zeros_like(self.v_template))
else:
# 使用encoder
self.displacementEncoder = DisplacementEncoder(
encoder=encoder_type, num_players=num_players)
多种编码方式:uv encoder、hash encoder…
Since our animatable 3D Gaussian representation is initialized by a standard human body model, the centers of 3D Gaussians are uniformly distributed near the human surface. We only need to sample at fixed positions near the surface of the human body in the parameter fields. This allows for significant compression of the hash table for the hash encoding [36]. Thus, we choose the hash encoding to model our parameter field to reduce the time and storage consumption.
class DisplacementEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder="uv", num_players=1):
super().__init__()
self.num_players = num_players
if encoder == "uv":
self.input_channels = 2
self.encoder = UVEncoder(
3, num_players=num_players)
elif encoder == "hash":
self.input_channels = 3
self.encoder = HashEncoder(
3, num_players=num_players)
elif encoder == "triplane":
self.input_channels = 3
self.encoder = TriPlaneEncoder(
3, num_players=num_players)
else:
raise Exception("encoder does not exist!")
这里先选择hash编码,使用tcnn
class HashEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_channels, num_players=1):
super().__init__()
self.networks = []
self.num_players = num_players
for i in range(num_players):
self.networks.append(tcnn.NetworkWithInputEncoding(
n_input_dims=3,
n_output_dims=num_channels,
encoding_config={
"otype": "HashGrid",
"n_levels": 16,
"n_features_per_level": 4,
"log2_hashmap_size": 17,
"base_resolution": 4,
"per_level_scale": 1.5,
},
network_config={
"otype": "FullyFusedMLP",
"activation": "ReLU",
"output_activation": "None",
"n_neurons": 64,
"n_hidden_layers": 2,
}
))
self.networks = nn.ModuleList(self.networks)
定义颜色、透明度、缩放、旋转:
rendering based on 3D Gaussian rasterization can only backpropagate the gradient to a finite number of Gaussians in a single iteration, which leads to a slow or even divergent optimization process for dynamic scenes. To address this issue, we suggest sampling spherical harmonic coefficients SH for each vertex from a continuous parameter field, which is able to affect all neighboring Gaussians in a single optimization.
Optionally, we provide UV-encoded spherical harmonic coefficients, allowing fast processing of custom human models with UV coordinate mappings. UV encoding potentially achieves higher reconstruction quality compared to hash encoding.
n = self.v_template.shape[1] * num_players # 总顶点数
# x0 → SH
if use_point_color:
self.shs_dc = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(
[n, 1, 3]))
self.shs_rest = nn.Parameter(torch.zeros(
[n, (max_sh_degree + 1) ** 2 - 1, 3]))
else:
# 使用encoder
self.shEncoder = SHEncoder(max_sh_degree=max_sh_degree,
encoder=encoder_type, num_players=num_players)
self.opacity = nn.Parameter(inverse_sigmoid(
0.2 * torch.ones((n, 1), dtype=torch.float)))
self.scales = nn.Parameter(
torch.log(torch.sqrt(dist2)).repeat([num_players, 1]))
rotations = torch.zeros([n, 4])
rotations[:, 0] = 1
self.rotations = nn.Parameter(rotations)
遮挡处理:x0, γ(t) → ao
We propose a time-dependent ambient occlusion module to address the issue of dynamic shadows in specific scenes.
if enable_ambient_occlusion:
self.aoEncoder = AOEncoder(
encoder=encoder_type, max_freq=max_freq, num_players=num_players)
self.register_buffer("aos", torch.ones_like(self.opacity))

we also employ hash encoding for the ambient occlusion ao, since shadows should be continuously modeled in space
class AOEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, encoder="uv", num_players=1, max_freq=4):
super().__init__()
self.num_players = num_players
self.max_freq = max_freq
if encoder == "uv":
self.input_channels = 2
self.encoder = UVTimeEncoder(
1, num_players=num_players, time_dim=max_freq*2 + 1)
elif encoder == "hash":
self.input_channels = 3
self.encoder = HashTimeEncoder(
1, num_players=num_players, time_dim=max_freq*2 + 1)
else:
raise Exception("encoder does not exist!")
class HashTimeEncoder(nn.Module):
def __init__(self, num_channels, time_dim=9, num_players=1):
super().__init__()
self.networks = []
self.time_nets = []
self.num_players = num_players
for i in range(num_players):
self.networks.append(tcnn.Encoding(
n_input_dims=3,
encoding_config={
"otype": "HashGrid",
"n_levels": 16,
"n_features_per_level": 4,
"log2_hashmap_size": 19,
"base_resolution": 4,
"per_level_scale": 1.5,
},
))
self.time_nets.append(tcnn.Network(
n_input_dims=self.networks[i].n_output_dims + time_dim,
n_output_dims=num_channels,
network_config={
"otype": "FullyFusedMLP",
"activation": "ReLU",
"output_activation": "None",
"n_neurons": 64,
"n_hidden_layers": 2,
}
))
self.networks = nn.ModuleList(self.networks)
self.time_nets = nn.ModuleList(self.time_nets)
至此,高斯球定义完成。
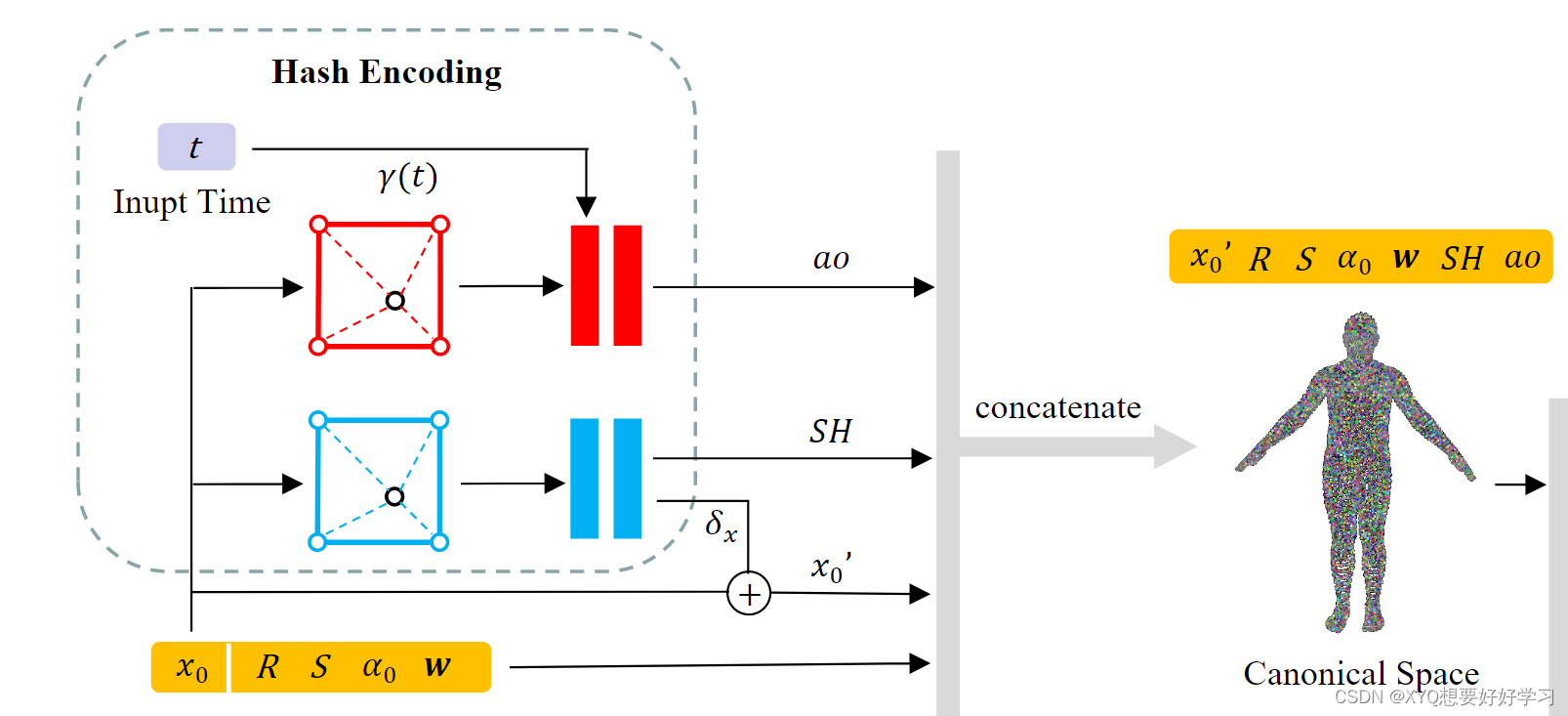
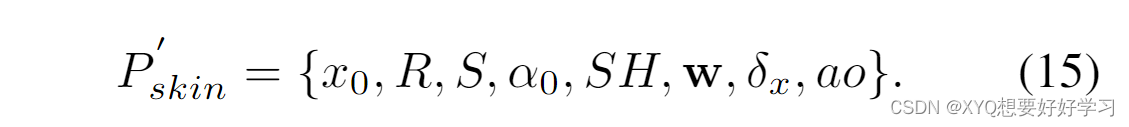
【pytorch】Animatable 3D Gaussian+源码解读(二)将进一步介绍数据集的处理细节。
智能推荐
使用nginx解决浏览器跨域问题_nginx不停的xhr-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1k次。通过使用ajax方法跨域请求是浏览器所不允许的,浏览器出于安全考虑是禁止的。警告信息如下:不过jQuery对跨域问题也有解决方案,使用jsonp的方式解决,方法如下:$.ajax({ async:false, url: 'http://www.mysite.com/demo.do', // 跨域URL ty..._nginx不停的xhr
在 Oracle 中配置 extproc 以访问 ST_Geometry-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2k次。关于在 Oracle 中配置 extproc 以访问 ST_Geometry,也就是我们所说的 使用空间SQL 的方法,官方文档链接如下。http://desktop.arcgis.com/zh-cn/arcmap/latest/manage-data/gdbs-in-oracle/configure-oracle-extproc.htm其实简单总结一下,主要就分为以下几个步骤。..._extproc
Linux C++ gbk转为utf-8_linux c++ gbk->utf8-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.5w次。linux下没有上面的两个函数,需要使用函数 mbstowcs和wcstombsmbstowcs将多字节编码转换为宽字节编码wcstombs将宽字节编码转换为多字节编码这两个函数,转换过程中受到系统编码类型的影响,需要通过设置来设定转换前和转换后的编码类型。通过函数setlocale进行系统编码的设置。linux下输入命名locale -a查看系统支持的编码_linux c++ gbk->utf8
IMP-00009: 导出文件异常结束-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读750次。今天准备从生产库向测试库进行数据导入,结果在imp导入的时候遇到“ IMP-00009:导出文件异常结束” 错误,google一下,发现可能有如下原因导致imp的数据太大,没有写buffer和commit两个数据库字符集不同从低版本exp的dmp文件,向高版本imp导出的dmp文件出错传输dmp文件时,文件损坏解决办法:imp时指定..._imp-00009导出文件异常结束
python程序员需要深入掌握的技能_Python用数据说明程序员需要掌握的技能-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读143次。当下是一个大数据的时代,各个行业都离不开数据的支持。因此,网络爬虫就应运而生。网络爬虫当下最为火热的是Python,Python开发爬虫相对简单,而且功能库相当完善,力压众多开发语言。本次教程我们爬取前程无忧的招聘信息来分析Python程序员需要掌握那些编程技术。首先在谷歌浏览器打开前程无忧的首页,按F12打开浏览器的开发者工具。浏览器开发者工具是用于捕捉网站的请求信息,通过分析请求信息可以了解请..._初级python程序员能力要求
Spring @Service生成bean名称的规则(当类的名字是以两个或以上的大写字母开头的话,bean的名字会与类名保持一致)_@service beanname-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读7.6k次,点赞2次,收藏6次。@Service标注的bean,类名:ABDemoService查看源码后发现,原来是经过一个特殊处理:当类的名字是以两个或以上的大写字母开头的话,bean的名字会与类名保持一致public class AnnotationBeanNameGenerator implements BeanNameGenerator { private static final String C..._@service beanname
随便推点
二叉树的各种创建方法_二叉树的建立-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读6.9w次,点赞73次,收藏463次。1.前序创建#include<stdio.h>#include<string.h>#include<stdlib.h>#include<malloc.h>#include<iostream>#include<stack>#include<queue>using namespace std;typed_二叉树的建立
解决asp.net导出excel时中文文件名乱码_asp.net utf8 导出中文字符乱码-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读7.1k次。在Asp.net上使用Excel导出功能,如果文件名出现中文,便会以乱码视之。 解决方法: fileName = HttpUtility.UrlEncode(fileName, System.Text.Encoding.UTF8);_asp.net utf8 导出中文字符乱码
笔记-编译原理-实验一-词法分析器设计_对pl/0作以下修改扩充。增加单词-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.1k次,点赞4次,收藏23次。第一次实验 词法分析实验报告设计思想词法分析的主要任务是根据文法的词汇表以及对应约定的编码进行一定的识别,找出文件中所有的合法的单词,并给出一定的信息作为最后的结果,用于后续语法分析程序的使用;本实验针对 PL/0 语言 的文法、词汇表编写一个词法分析程序,对于每个单词根据词汇表输出: (单词种类, 单词的值) 二元对。词汇表:种别编码单词符号助记符0beginb..._对pl/0作以下修改扩充。增加单词
android adb shell 权限,android adb shell权限被拒绝-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读773次。我在使用adb.exe时遇到了麻烦.我想使用与bash相同的adb.exe shell提示符,所以我决定更改默认的bash二进制文件(当然二进制文件是交叉编译的,一切都很完美)更改bash二进制文件遵循以下顺序> adb remount> adb push bash / system / bin /> adb shell> cd / system / bin> chm..._adb shell mv 权限
投影仪-相机标定_相机-投影仪标定-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读6.8k次,点赞12次,收藏125次。1. 单目相机标定引言相机标定已经研究多年,标定的算法可以分为基于摄影测量的标定和自标定。其中,应用最为广泛的还是张正友标定法。这是一种简单灵活、高鲁棒性、低成本的相机标定算法。仅需要一台相机和一块平面标定板构建相机标定系统,在标定过程中,相机拍摄多个角度下(至少两个角度,推荐10~20个角度)的标定板图像(相机和标定板都可以移动),即可对相机的内外参数进行标定。下面介绍张氏标定法(以下也这么称呼)的原理。原理相机模型和单应矩阵相机标定,就是对相机的内外参数进行计算的过程,从而得到物体到图像的投影_相机-投影仪标定
Wayland架构、渲染、硬件支持-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.2k次。文章目录Wayland 架构Wayland 渲染Wayland的 硬件支持简 述: 翻译一篇关于和 wayland 有关的技术文章, 其英文标题为Wayland Architecture .Wayland 架构若是想要更好的理解 Wayland 架构及其与 X (X11 or X Window System) 结构;一种很好的方法是将事件从输入设备就开始跟踪, 查看期间所有的屏幕上出现的变化。这就是我们现在对 X 的理解。 内核是从一个输入设备中获取一个事件,并通过 evdev 输入_wayland