《笨办法学python》习题31-35_32.if a = [1,2,3,4,5; 3,4,5,6,7], then the value o-程序员宅基地
技术标签: python
习题31:作出决定
代码
print("""You enter a dark room with two doors.
Do you go through door #1 or door #2?""")
door = input(">")
if door == "1":
print("There's a giant bear here eating a cheese cake.")
print("What do you da?")
print("1.Take the cake.")
print("2.Scream at the bear.")
bear = input(">")
if bear == "1":
print("The bear eats your face off.Good job!")
elif bear == "2":
print("The bear eats your legs off.Good job!")
else:
print(f"Well,doing {bear} is probably better.")
print("Bear runs away.")
elif door == "2":
print("You stare into the endless abyss at cthulhu's retina")
print("1.Blueberries.")
print("2.Yellow jacket clothespins.")
print("3.Understanding revolver yelling melogies.")
insanity = input(">")
if insanity == "1" or insanity == "2":
print("Your body survives powered by a mind of jello.")
print("Good job!")
else:
print("The insanity rots your eyes into a pool of muck.")
print("Good job!")
else:
print("Your stumble around and fall on a knife and die.Good job!")
PS C:\Users\WU\pyfile> python ex31.py
You enter a dark room with two doors.
Do you go through door #1 or door #2?
>1
There's a giant bear here eating a cheese cake.
What do you da?
1.Take the cake.
2.Scream at the bear.
>2
The bear eats your legs off.Good job!
横竖都得死。。。
知识点
- 使用1<x<10 或 1<= x <10 ,或者x in range (1,10)这种经典语法去判定一个数是否处于某个值域。
- if-elif-else 还可以继续增加为 if-elif-elif-elif-else 等等。
- if语句内部还有一个if语句作为可运行的代码,这种嵌套的手法把一个分支引向另一个分支的子分支。
- elif必须和if一起使用,否则出错。else 一般用在最后,即所有条件都不满足时使用。
- if-else组合是可以替代elif的。不过python只有遇到第一个True就停下当前判断。这篇if-else-elif-if嵌套比较清晰一些。
习题32:循环和列表
代码
the_count = [1,2,3,4,5]
fruits = ['apple','oranges','pears','apricots']
change= [1,'pennies',2,'dimes',3,'quarters']
#this first kind of for-loop goes through a list
for number in the_count:
print(f"This is count {number}")
# same as above
for fruit in fruits:
print(f"A fruit if type : {fruit}")
#also we can go through mixed lists too
#notice we have to use {} since we don't know what's in it
for i in change:
print(f"I got {i}")
# we can also build lists,first start with an empty one
elements = []
#then use the range function to do 0 to 5 coounts
for i in range(0,6):
print(f"Adding {i} to the list.")
#append is a function that lists understand
elements.append(i)
#now we can print them out too
for i in elements:
print(f"Element was :{i}")
PS C:\Users\WU> cd pyfile
PS C:\Users\WU\pyfile> python ex32.py
This is count 1
This is count 2
This is count 3
This is count 4
This is count 5
A fruit if type : apple
A fruit if type : oranges
A fruit if type : pears
A fruit if type : apricots
I got 1
I got pennies
I got 2
I got dimes
I got 3
I got quarters
Adding 0 to the list.
Adding 1 to the list.
Adding 2 to the list.
Adding 3 to the list.
Adding 4 to the list.
Adding 5 to the list.
Element was :0
Element was :1
Element was :2
Element was :3
Element was :4
Element was :5
知识点
- 列表(list)创建方式: list = [a,b,c,d,e,f] 左方括号 “[” 表示“打开”列表,逗号隔开元素,右边括号 “]” 表明列表结束。
- range的功能:回一个递进的整数的列表。range的用法:range(起始位,结束位,步数),注意range的起始位和结束位构成的区间是一个前闭后开的,即range()函数会从第一个数到最后一个数,但不包含最后一个数字。例如range(0,10,2)是[0,2,4,6,8] .
- [[0,1,2],[0,1,2]] 这是二维列表,即列表中包含列表。
- for value in variable: 中value变量在for循环开始就已经被创立,每次循环value都会被重新初始化为当前循环中的 元素值。
| 函数 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| cmp(list1, list2) | 比较两个列表的元素 |
| len(list) | 列表元素个数 |
| max(list) | 返回列表元素最大值 |
| min(list) | 返回列表元素最小值 |
| list(seq) | 将元组转换为列表 |
| list.append(obj) | 在列表末尾添加新的对象 |
| list.count(obj) | 统计某个元素在列表中出现的次数 |
| list.extend(seq) | 在列表末尾一次性追加另一个序列中的多个值(用新列表扩展原来的列表) |
| list.index(obj) | 从列表中找出某个值第一个匹配项的索引位置 |
| list.insert(index, obj) | 将对象插入列表 |
| list.pop([index=-1]) | 移除列表中的一个元素(默认最后一个元素),并且返回该元素的值 |
| list.remove(obj) | 移除列表中某个值的第一个匹配项 |
| list.reverse() | 反向列表中元素 |
| list.sort(cmp=None, key=None, reverse=False) | 对原列表进行排序 |
习题33:while循环
代码
from typing import Sequence
i = 0
numbers = []
Seq = 5
while i < 6:
print(f"At the top i is {i}")
numbers.append(i)
i += Seq
print(f"At the bottom i is {i}")
print("The numbers:")
for num in numbers:
print(num)
PS C:\Users\WU\pyfile> python ex33.py
At the top i is 0
At the bottom i is 1
At the top i is 1
At the bottom i is 2
At the top i is 2
At the bottom i is 3
At the top i is 3
At the bottom i is 4
At the top i is 4
At the bottom i is 5
At the top i is 5
At the bottom i is 6
The numbers:
0
1
2
3
4
5
def app(steps,max):
numbers = []
i = 0
while i < max:
numbers.append(i)
i += steps
print(numbers)
app(2,10)
PS C:\Users\WU> & python c:/Users/WU/pyfile/py33test.py
[0]
[0, 2]
[0, 2, 4]
[0, 2, 4, 6]
[0, 2, 4, 6, 8]
知识点
- ctrl C 终止循环
- while循环有时候会永远无法停止。注意尽量少用while 循环,大部分时候for 循环 是更好的选择。重复检查你的while语句,确定测试的布尔表达式最终会变成False。如果不确定,就在while 循环的开始和结尾打印出你要测试的值,看看它的变化
- for循环只能对一些东西的集合进行循环,while 循环可以对任何对象进行循环。然而,相比起来while 循环更难弄对,而对一般任务用 for 循环更容易一些。
- while语义很简单,但条件判断为True 时,循环重复执行语句块中的语句;当条件为False时,循环终止,执行与while同级别缩进的后续语句。
- while 还可以和else结合
while <语句>:
<语句块1>
else:
<语句块2>
习题34:访问列表的元素
代码
animals = ["bear",'python',"peacock","kangeroo","whale","platypous"]
print("位置1:"+animals[1])
print("第3只:"+animals[2])
print("第一只:"+animals[0])
print("位置3:"+animals[3])
print("第5只:"+animals[4])
print("位置3:"+animals[3])
print("第6只:"+animals[5])
print("位置4:"+animals[4])
PS C:\Users\WU> & python c:/Users/WU/pyfile/ex34.py
位置1:python
第3只:peacock
第一只:bear
位置3:kangeroo
第5只:whale
位置3:kangeroo
第6只:platypous
位置4:whale
知识点
- 简单地说序数从1开始,基数从0开始,序数符合人类的思维,基数符合计算机的思维。序数(ordinal number):从1开始编号,表示事物的顺序
- 基数(cardinal number):从0开始,表示你可以任意抓取元素
- 序数(ordinal number):从1开始编号,表示事物的顺序
习题35:分支和函数
代码
from sys import exit
from typing import DefaultDict
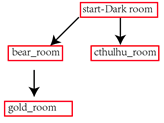
def gold_room():
print("This room is full of gold. How much do you take?")
choice = input(">")
if "0" in choice or "1" in choice:
how_much = int(choice)
else:
dead("Man,learn to type a number.")
if how_much < 50 :
print("Nice,you're not greedy,you win!")
exit(0)
else:
dead("You greedy bastard!")
def bear_room():
print("There is a bear here.")
print("The bear has a bunch of honey.")
print("The fat bear is in front of another door.")
print("How are you going to move the bear?")
bear_moved = False
while True:
choice = input("> ")
if choice == "take money":
dead("The bear looks at you then slaps your face off.")
elif choice == "taunt bear" and not bear_moved:
print("The bear has moved from the door.")
print("You can go through it now.")
bear_moved = True
elif choice == "taunt bear" and bear_moved:
dead ("The bear gets pissed off and chews your legs off.")
elif choice == "open door" and bear_moved:
gold_room()
else:
print("I got no idea what that means.")
def cthulhu_room():
print("Here you see the grear evil Cthulhu.")
print("He,it,Whatever stares at you and you go insane.")
print("Do you flee for youe life or eat your head?")
choice = input("> ")
if "flee" in choice:
start()
elif "head" in choice:
dead("Well that was tasty!")
else:
cthulhu_room()
def dead(why):
print(why ,"Good job!")
exit(0)
def start():
print("You are in a dark room.")
print("There is a door to your right and left.")
print("Which one do you take?")
choice = input("> ")
if choice == "left":
bear_room()
elif choice == "right":
cthulhu_room()
else:
dead("You stumble around the room until you starve")
start()
PS C:\Users\WU\pyfile> python ex35.py
You are in a dark room.
There is a door to your right and left.
Which one do you take?
> left
There is a bear here.
The bear has a bunch of honey.
The fat bear is in front of another door.
How are you going to move the bear?
> taunt bear
The bear has moved from the door.
You can go through it now.
> open the door
I got no idea what that means.
> open door
This room is full of gold. How much do you take?
>25
Man,learn to type a number. Good job!
知识点
· 
- while True表示一个无限循环。
- exit(0) 可以终止某个程序,而其中的数字参数则用来表示是否遇到错误而终止。exit(1) (或大于 1)表示程序执行失败发生错误并退出程序,而exit(0) 则表示程序是正常退出的。
- input(“> ”)里面的>是用来提示用户输入的,比较人机交互吧。
智能推荐
攻防世界_难度8_happy_puzzle_攻防世界困难模式攻略图文-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读645次。这个肯定是末尾的IDAT了,因为IDAT必须要满了才会开始一下个IDAT,这个明显就是末尾的IDAT了。,对应下面的create_head()代码。,对应下面的create_tail()代码。不要考虑爆破,我已经试了一下,太多情况了。题目来源:UNCTF。_攻防世界困难模式攻略图文
达梦数据库的导出(备份)、导入_达梦数据库导入导出-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.9k次,点赞3次,收藏10次。偶尔会用到,记录、分享。1. 数据库导出1.1 切换到dmdba用户su - dmdba1.2 进入达梦数据库安装路径的bin目录,执行导库操作 导出语句:./dexp cwy_init/[email protected]:5236 file=cwy_init.dmp log=cwy_init_exp.log 注释: cwy_init/init_123..._达梦数据库导入导出
js引入kindeditor富文本编辑器的使用_kindeditor.js-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.9k次。1. 在官网上下载KindEditor文件,可以删掉不需要要到的jsp,asp,asp.net和php文件夹。接着把文件夹放到项目文件目录下。2. 修改html文件,在页面引入js文件:<script type="text/javascript" src="./kindeditor/kindeditor-all.js"></script><script type="text/javascript" src="./kindeditor/lang/zh-CN.js"_kindeditor.js
STM32学习过程记录11——基于STM32G431CBU6硬件SPI+DMA的高效WS2812B控制方法-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.3k次,点赞6次,收藏14次。SPI的详情简介不必赘述。假设我们通过SPI发送0xAA,我们的数据线就会变为10101010,通过修改不同的内容,即可修改SPI中0和1的持续时间。比如0xF0即为前半周期为高电平,后半周期为低电平的状态。在SPI的通信模式中,CPHA配置会影响该实验,下图展示了不同采样位置的SPI时序图[1]。CPOL = 0,CPHA = 1:CLK空闲状态 = 低电平,数据在下降沿采样,并在上升沿移出CPOL = 0,CPHA = 0:CLK空闲状态 = 低电平,数据在上升沿采样,并在下降沿移出。_stm32g431cbu6
计算机网络-数据链路层_接收方收到链路层数据后,使用crc检验后,余数为0,说明链路层的传输时可靠传输-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.2k次,点赞2次,收藏8次。数据链路层习题自测问题1.数据链路(即逻辑链路)与链路(即物理链路)有何区别?“电路接通了”与”数据链路接通了”的区别何在?2.数据链路层中的链路控制包括哪些功能?试讨论数据链路层做成可靠的链路层有哪些优点和缺点。3.网络适配器的作用是什么?网络适配器工作在哪一层?4.数据链路层的三个基本问题(帧定界、透明传输和差错检测)为什么都必须加以解决?5.如果在数据链路层不进行帧定界,会发生什么问题?6.PPP协议的主要特点是什么?为什么PPP不使用帧的编号?PPP适用于什么情况?为什么PPP协议不_接收方收到链路层数据后,使用crc检验后,余数为0,说明链路层的传输时可靠传输
软件测试工程师移民加拿大_无证移民,未受过软件工程师的教育(第1部分)-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读587次。软件测试工程师移民加拿大 无证移民,未受过软件工程师的教育(第1部分) (Undocumented Immigrant With No Education to Software Engineer(Part 1))Before I start, I want you to please bear with me on the way I write, I have very little gen...
随便推点
Thinkpad X250 secure boot failed 启动失败问题解决_安装完系统提示secureboot failure-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读304次。Thinkpad X250笔记本电脑,装的是FreeBSD,进入BIOS修改虚拟化配置(其后可能是误设置了安全开机),保存退出后系统无法启动,显示:secure boot failed ,把自己惊出一身冷汗,因为这台笔记本刚好还没开始做备份.....根据错误提示,到bios里面去找相关配置,在Security里面找到了Secure Boot选项,发现果然被设置为Enabled,将其修改为Disabled ,再开机,终于正常启动了。_安装完系统提示secureboot failure
C++如何做字符串分割(5种方法)_c++ 字符串分割-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读10w+次,点赞93次,收藏352次。1、用strtok函数进行字符串分割原型: char *strtok(char *str, const char *delim);功能:分解字符串为一组字符串。参数说明:str为要分解的字符串,delim为分隔符字符串。返回值:从str开头开始的一个个被分割的串。当没有被分割的串时则返回NULL。其它:strtok函数线程不安全,可以使用strtok_r替代。示例://借助strtok实现split#include <string.h>#include <stdio.h&_c++ 字符串分割
2013第四届蓝桥杯 C/C++本科A组 真题答案解析_2013年第四届c a组蓝桥杯省赛真题解答-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读2.3k次。1 .高斯日记 大数学家高斯有个好习惯:无论如何都要记日记。他的日记有个与众不同的地方,他从不注明年月日,而是用一个整数代替,比如:4210后来人们知道,那个整数就是日期,它表示那一天是高斯出生后的第几天。这或许也是个好习惯,它时时刻刻提醒着主人:日子又过去一天,还有多少时光可以用于浪费呢?高斯出生于:1777年4月30日。在高斯发现的一个重要定理的日记_2013年第四届c a组蓝桥杯省赛真题解答
基于供需算法优化的核极限学习机(KELM)分类算法-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读851次,点赞17次,收藏22次。摘要:本文利用供需算法对核极限学习机(KELM)进行优化,并用于分类。
metasploitable2渗透测试_metasploitable2怎么进入-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读1.1k次。一、系统弱密码登录1、在kali上执行命令行telnet 192.168.26.1292、Login和password都输入msfadmin3、登录成功,进入系统4、测试如下:二、MySQL弱密码登录:1、在kali上执行mysql –h 192.168.26.129 –u root2、登录成功,进入MySQL系统3、测试效果:三、PostgreSQL弱密码登录1、在Kali上执行psql -h 192.168.26.129 –U post..._metasploitable2怎么进入
Python学习之路:从入门到精通的指南_python人工智能开发从入门到精通pdf-程序员宅基地
文章浏览阅读257次。本文将为初学者提供Python学习的详细指南,从Python的历史、基础语法和数据类型到面向对象编程、模块和库的使用。通过本文,您将能够掌握Python编程的核心概念,为今后的编程学习和实践打下坚实基础。_python人工智能开发从入门到精通pdf